- Help Center
- EMA3D
-
Getting Started With Ansys
-
Ansys Installation
-
Licensing
-
Ansys Mechanical
-
ANSYS AEDT
-
Ansys Maxwell
-
Ansys HFSS
-
Ansys CFD
-
CAD
-
Meshing
-
LS-Dyna & LS-Prepost
-
SpaceClaim
-
Ensight
-
Ansys Lumerical
-
Zemax
-
Discovery
-
AUTODYN
-
Workbench
-
Ansys EMC Plus
-
SIwave
-
CFD-Post
-
Ansys Sherlock
-
Q3D
-
Ansys 3D Layout
-
Fluent Meshing
-
Thermal Desktop
-
Icepak
-
Ansys Icepak
-
Twin Builder
-
Fluent
-
AEDT Circuit
-
EMA3D
-
Linux
-
Optislang
-
Motor-CAD
-
Ansys CFX
How is HPC / Parallel Computing set up?
How to use HPC / set up parallel computing in EMC Plus / Charge Plus.
Answer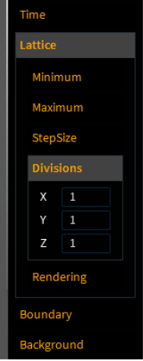
EMA3D is fully parallelized using the industry-standard Message Passing Interface (MPI), specifically version 2.2. This allows the software to execute a single simulation across any number of available processor cores.
The method used to achieve this is known as domain decomposition. The software takes the entire finite-difference problem space—the large rectangular volume that contains your model—and divides it into smaller, adjacent volumetric regions. These smaller regions are called MPI blocks.
Each MPI block is then assigned to a single processor core. The solver works on all these blocks concurrently, with each core responsible for calculating the fields within its assigned block. The MPI standard manages the communication between the processors, ensuring that the field information at the boundaries of each block is correctly passed to its neighbors at each time step.
How to Configure Parallel Processing
You have direct control over how the simulation domain is divided for parallel processing.
In the Graphical User Interface (GUI):
- Navigate to the Domain properties panel, which you can access by clicking "Domain" in the EMA3D ribbon.
- Select the Lattice tab.
- Here you will find the "Parallel Divisions" settings for the X, Y, and Z directions.
You specify the number of blocks (divisions) you want to create along each of the three Cartesian axes. The total number of processor cores that the simulation will use is the product of these three numbers (X divisions × Y divisions × Z divisions). For example, setting the divisions to 4, 2, and 2 would divide the problem into 16 MPI blocks and utilize 16 processor cores.
In the Input File (.emin):
For advanced users or for scripting purposes, this setting is controlled directly in the .emin input file. It is one of the first general keywords in the file. 
A screenshot of a computer code
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
Keyword: !MPIBLOCKS
Parameters: Nx Ny Nz
Here, Nx, Ny, and Nz are integer values representing the number of blocks you want to create in the x, y, and z-directions, respectively.
-2.png?height=120&name=Ozen%20Long%20-%20Back%20(1)-2.png)